Architecture Weekly Issue #140. Articles, books, and playlists on architecture and related topics. Split by sections, highlighted with complexity: 🤟 means hardcore, 👷♂️ is technically applicable right away, 🍼 - is an introduction to the topic or an overview. Now in telegram and Substack as well.
Sponsored
Depot Managed GitHub Actions runners offer caching that's 10x faster than GitHub's own solution, and at half the cost. It’s the secret to boosting your CI/CD pipelines without breaking the bank. Find out how it works!
Highlights
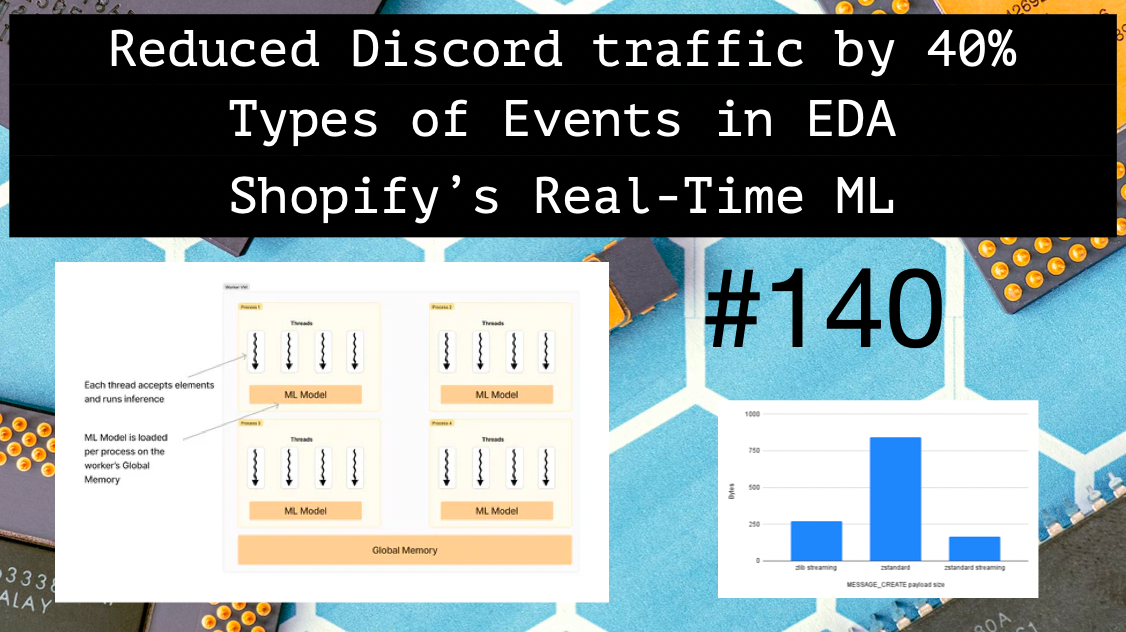
How Discord Reduced Websocket Traffic by 40% 👷♂️
TL;DR: Discord tried a new compression algorithm, failed initially but then was extremely successful. At the same time the article is the fun read with technical details on the usage of dictionaries in data compression and learnings about roll-outs.

#performance
The different types of events in event-driven systems 🍼
When building event-driven systems you can use events that contain all the information that potentially can be useful. On the other side of the spectrum you can just an event with the related entity id. What should you do? Frand de Jonge demonstrates three types of events and compares their pros and cons

#ddd
How Shopify improved consumer search intent with real-time ML 👷♂️
We used to write "jeans" or "hat" in the search bar in e-Commerce, but what if we could write "Warm teenage clothes for winter" instead? This is what Shopify rolled out with real-time ML. Find the deeply technical article how it was made possible.

#ml #casestudy
Follow-Up
Examples of Zero-Knowledge proofs 🍼
Zero knowledge is a useful cybersecurity concept yet to be widely adopted. Nevertheless, it's worth to understand the examples of the proofs that can be presented to show that one pocesses a secret without revealing it. Follow the article for such examples(Waldo inside!)
#security
Crafting the Ultimate Docker Image for Spring Applications 👷♂️
Recently we read about how AWS Lamda sped up the cold start of functions via caching of docker layers; apparently you can apply the same approach for your own apps to optimize the pull size. Pasha Finkelstein shows how to do that in his deck.
#performance
Testing a React App in Chrome 👷♂️
End-to-end tests is a good way to ensure that the app's basic scenarios are operational. But you can't rely on tests running on local machines; you rather need to run those tests on CI. Heroku shared how it can be done on general CI and on Heroku CI as well.

#quality
Dead code, Zombie servers 🍼
The rare topic as it is, but have you thought how bad of underutilization are your apps and servers? Holly Cummins shares some statistics about the average server running at 18% capacity still consuming 60% of maximum power. That's sad and probably at the Halloween Eve we should about lean usage of resource once more.

#sustainability
Scalability! But at what COST? 🤟
The paper introduces the concept of "COST" (Configuration that Outperforms a Single Thread) as a metric to evaluate the true performance of scalable big data systems. COST assesses how much hardware is required for a distributed system to surpass the performance of a single-threaded implementation. The authors highlight that many distributed systems exhibit high COST due to excessive parallelization overhead, questioning the actual performance benefits of such systems compared to simple, single-threaded alternatives.
#paper #scalability